作用域与闭包 讲解 this, var, (function(){})
知识点
理解js中var的作用域
了解闭包的概念
理解this的指向
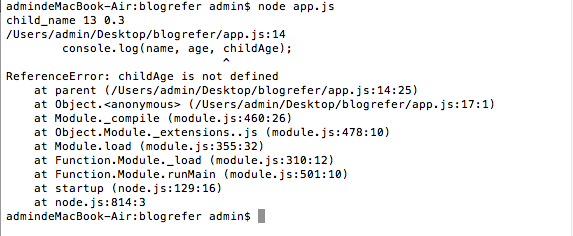
课程内容 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 var parent = function () { var name = "parent_name"; var age = 13; var child = function () { var name = "child_name"; var childAge = 0.3; console.log(name, age, childAge); }; child(); console.log(name, age, childAge); }; parent();
学过一点别的编程语言肯定都会直觉的认为,内部函数可以访问外部函数的变量,外部不能访问内部函数的变量.因此childAge在parent中会报错.如果声明变量是少了var,就声明就全局变量了.
如果使用Sublime Text,可以按照SublimeLinter插件,进行错误检测,默认使用JSHint作为JavaScript校验器Mac OS X, Sublime text 2->Preferences->Package Setting->SublimeLinter->Setting - User配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 { "sublimelinter": "save-only", //运行模式 "sublimelinter_popup_errors_on_save": true, "sublimelinter_executable_map": { "javascript": "D:/Program Files/nodejs/node.exe", "css": "D:/Program Files/nodejs/node.exe" }, "jshint_options": { "strict": false, "quotmark": "single", //只能使用单引号 "noarg": true, "noempty": true, //不允许使用空语句块{} "eqeqeq": true, //!==和===检查 "undef": true, "curly": true, //值为true时,不能省略循环和条件语句后的大括号 "forin": true, //for in hasOwnPropery检查 "devel": true, "jquery": true, "browser": true, "wsh": true, "evil": true, "unused": "vars", //形参和变量未使用检查 "latedef": true, //先定义变量,后使用 "globals": { "grunt": true, "module": true, "window": true, "jQuery": true, "$": true, "global": true, "document": true, "console": true, "setTimeout": true, "setInterval": true } }, "csslint_options": { "adjoining-classes": false, "box-sizing": false, "box-model": false, "compatible-vendor-prefixes": false, "floats": false, "font-sizes": false, "gradients": false, "important": false, "known-properties": false, "outline-none": false, "qualified-headings": false, "regex-selectors": false, "shorthand": false, "text-indent": false, "unique-headings": false, "universal-selector": false, "unqualified-attributes": false } }
1 2 3 4 5 SublimeLinter 的运行模式,总共有四种,含义分别如下: true - 在用户输入时在后台进行即时校验 false - 只有在初始化的时候才进行校验 "load-save" - 当文件加载和保存的时候进行校验 "save-only" - 当文件被保存的时候进行校验
校验引擎,Mac下使用which node获取路径
1 2 3 4 5 "sublimelinter_executable_map": { "javascript":"/usr/local/bin/node", "css":"/usr/local/bin/node" }
更多的请参考文档: http://jshint.com/docs/#options 作者英文只有小学一级,搞不定
在JavaScript中,变量的局部作用域是函数级别的.不同于C语言,在C语言中作用域是块级别.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 function foo() { for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) { var value = "hello world"; } console.log(i); console.log(value); } foo();
所以我们养成一个好习惯,提前声明
闭包 http://coolshell.cn/articles/6731.html 这篇博客可以参考参考
1 2 3 4 5 for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) { setTimeout(function() { console.log(i); }, 5); }
程序不会按照我们预期的结果打印1 2 3 4 5.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) { (function(idx) { setTimeout(function() { console.log(idx); }, 5); })(i); }
程序变成这样,结果和预期一样
一些闭包的例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 /* //闭包中使用局部变量是引用而非直接拷贝 function s() { var num = 6; var sa = function() { console.log(num); }; num++; return sa; } var sa = s(); sa(); // ==> // 7 */ /* //多个函数绑定同一个闭包,引用同一个变量 function setupSomeGlobals () { var num = 666; gAlertNumber = function(){ console.log(num); }; gIncreaseNumber = function() { num++; }; gSetNumber = function(x) { num = x; }; } setupSomeGlobals(); gAlertNumber(); gIncreaseNumber(); gAlertNumber(); gSetNumber(18); gAlertNumber(); // ==> // 666 // 667 // 18 */ /* //当在一个循环中赋值函数时,这些函数将绑定同样的闭包,函数内使用了外部变量的引用 function buildList(list) { var result = []; for(var i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { var item = 'item' + list[i]; result.push(function(){ console.log(item + ' ' + list[i]); }); } return result; } function testList() { var fnlist = buildList([1, 2, 3]); for (var j = 0; j < fnlist.length; j++) { fnlist[j](); }; } testList(); */ // ==> // item3 undefined // item3 undefined // item3 undefined /* //外部函数所有局部变量都在闭包内,即使这个变量声明在内部函数定义之后 function sa() { var sas = function(){ console.log(alice); }; var alice = "Hello world"; return sas; } var hello = sa(); hello(); // ==> // Hello world */ /* // 每次函数调用的时候创建一个新的闭包 function newClosure(someNum, someRef) { var num = someNum; var anArray = [1, 2, 3]; var ref = someRef; return function(x) { num += x; anArray.push(num); console.log('num: ' + num + '\nanArray' + anArray.toString() + '\nref.someVar' + ref.someVar); }; } closure1 = newClosure(400, { someVar: 'closure 1'}); closure2 = newClosure(400, { someVar: 'closure 2'}); closure1(5); closure2(-10); // ==> // num: 405 // anArray1,2,3,405 // ref.someVarclosure 1 // num: 390 // anArray1,2,3,390 // ref.someVarclosure 2 */
this 在函数执行时,this总是指向调用该函数的对象.要判断this的指向,其实就是判断this所在的函数属于谁.
有对象就指向调用对象
没调用对象就指向全局对象
用new构造就指向新对象
通过apply或call或bind来改变this的所指
函数有所属对象是,通常通过.表达式调用,这时的this自然指向所属对象.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 var obj = { value : 100}; obj.getValue = function() { // { value: 100, getValue: [Function] } // 其实就是obj对象本身 console.log(this); return this.value; }; console.log(obj.getValue());
getValue()方法属于对象obj,有obj进行.调用,因此this指向对象obj
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 var obj = { value : 100}; obj.getValue = function() { var foo = function () { console.log(this.value); // => undefined console.log(this); // 全局global对象 }; foo(); return this.value; }; console.log(obj.getValue());
在上述代码块中,foo函数虽然定义在getValue的函数体内,但实际上它既不属于getValue也不属于obj.foo并没有绑定在任何对象上,所以当调用时,它的this指针指向了全局对象global.
js中,我们通过new关键词来调用构造函数,此时this会绑定在该新对象上.
1 2 3 4 5 var objClass = function () { this.value = 100; }; var create = new objClass(); console.log(create.value); // => 100
在js中,构造函数、普通函数、对象方法、闭包,这死者没有明确界线.
apply、call调用和bind绑定:指向绑定的对象
apply()方法接受两个参数,第一个是函数运行的作用域,另一个是参数数组(arguments)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 var obj = { value: 100 }; var foo = function () { console.log(this); }; foo(); //全局变量 global foo.apply(obj); foo.call(obj); var n = foo.bind(obj); n();