
第二天
格式化输出
必须显示添加换行符
1 | printf "Hello, Shell\n" |
printf命令语法:printf format-string [arguments...]
1 | #!/bin/bash |
if…else语句
if语句:
1 | if [ expression ] |
if…else语句:
1 | if [ expression ] |
多层使用:
1 | if [ expression 1 ] |
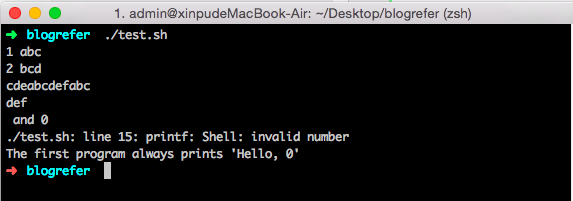
if…else语句也可以写成一行,以命令行的方式来运行1
if test $[2*3] -eq $[1+5]; then echo "The two numbers are equal!"; fi;
test命令用于检测条件是否成立,与方括号[]类似$[]还计算了结果保存到变量中
分支语句
1 | case 值 in |
1 | #!/bin/bash |
for循环
1 | for 变量 in 列表 |
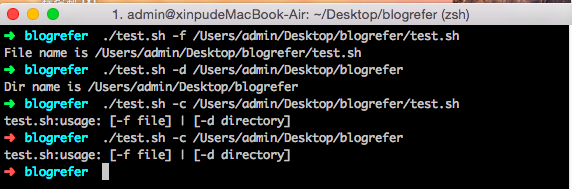
列表为一组值, 每个值通过空格分隔,每循环一次,就将列表中的下一个值赋给变量.
列表是可选的,如果不用它,for循环使用命令行的位置参数
显示主目录下以 .bash 开头的文件:
1 | #!/bin/bash |
while循环
1 | while 条件 |
until循环
1 | until 条件 |
1 | #!/bin/bash |
break 跳出循环
break n 跳出n层循环
continue 结束本次循环
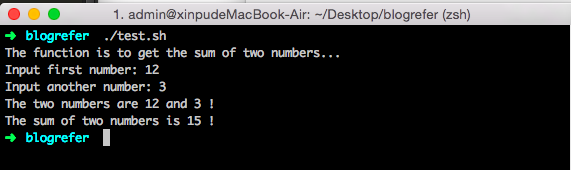
函数
1 | function_name(){ |
1 | #!/bin/bash |
1 | #!/bin/bash |
使用unset .f function_name来删除函数
如果你希望直接从终端调用函数,可以将函数定义在主目录下的 .profile 文件,这样每次登录后,在命令提示符后面输入函数名字就可以立即调用.
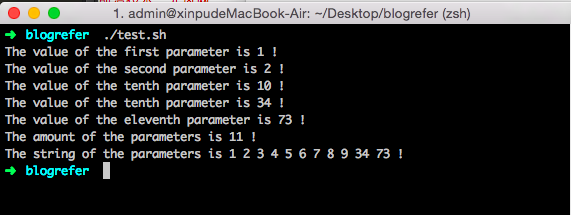
函数参数
1 | #!/bin/bash |
| 特殊变量 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| $# | 传递给函数的参数个数 |
| $* | 显示所有传递给函数的参数 |
| $@ | 与$*相同,但是略有区别,请查看Shell学习第一天 |
| $? | 函数的返回值 |
输入输出重定向
一般情况下,每个 Unix/Linux 命令运行时都会打开三个文件:
- 标准输入文件(stdin):stdin的文件描述符为0,Unix程序默认从stdin读取数据
- 标准输出文件(stdout):stdout 的文件描述符为1,Unix程序默认向stdout输出数据
- 标准错误文件(stderr):stderr的文件描述符为2,Unix程序会向stderr流中写入错误信息
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| command > file | 将输出重定向到 file |
| command < file | 将输入重定向到 file |
| command >> file | 将输出以追加的方式重定向到 file |
| n > file | 将文件描述符为 n 的文件重定向到 file |
| n >> file | 将文件描述符为 n 的文件以追加的方式重定向到 file |
| n >& m | 将输出文件 m 和 n 合并 |
| n <& m | 将输入文件 m 和 n 合并 |
| << tag | 将开始标记 tag 和结束标记 tag 之间的内容作为输入 |
如果希望执行某个命令,但又不希望在屏幕上显示输出结果,那么可以将输出重定向到 /dev/null:$ command > /dev/null
/dev/null是一个特殊的文件,写入到它的内容都会被丢弃;如果尝试从该文件读取内容,那么什么也读不到。但是 /dev/null 文件非常有用,将命令的输出重定向到它,会起到”禁止输出“的效果
如果希望屏蔽 stdout 和 stderr,可以这样写:$ command > /dev/null 2>&1
Here Document:
Here Document 目前没有统一的翻译,这里暂译为”嵌入文档“.Here Document 是 Shell 中的一种特殊的重定向方式,它的基本的形式如下:
1 | command << delimiter |
它的作用是将两个 delimiter 之间的内容(document) 作为输入传递给 command
文件包含
. filename或者source filename